On 1 July, Chichester MP Jess Brown-Fuller led her first adjournment debate in the House of Commons Chamber.
She raised key concerns with the Government, calling for a national strategy for England. In her role as chair of the All-Party Parliamentary Group (APPG) on Infant Feeding she focuses on specific policy areas, beyond her constituency work. She aims to hold the government to account, by raising identified gaps in policy with the relevant government minister. Such debates apply pressure to increase accountability so may lead to a change in the law.
Jess highlighted her own positive experience of a network of community support when her children were born a decade ago but which is now, at best, patchy or non-existent. She urged the government to implement all eleven Competition and Markets Authority (CMA) final report recommendations to protect families from the current unacceptable exploitation by the infant formula market.
Several MPs supported the debate by sharing both their own experiences and stories from constituents about the importance of skilled breastfeeding support.
WBTi in Parliament
For the first time, the WBTi report was mentioned by a minister on the floor of the House of Commons. Ashley Dalton, Parliamentary Under-Secretary of State for Public Health and Prevention in the Department of Health and Social Care, replied on behalf of the government:
“We recognise the concerns raised in the World Breastfeeding Trends Initiative’s United Kingdom report and are considering the recommendations” and “we know through the report that England scores poorly, and we want to change that.” See Column 260 in the Hansard report of the debate.
MPs who attended:
Maya Ellis, Labour MP Ribble Valley
Jim Shannon, DUP MP Strangford ( Northern Ireland )
Connor Rand, Labour MP Altrincham and Sale West
Samantha Niblett, Labour MP South Derbyshire
David Reed, Conservative MP Exmouth and Exeter East
David Chadwick, Liberal Democrat MP Brecon Radnor and Cwm Tawe (Wales)
Dr Danny Chamber, Liberal Democrat Winchester
Article in the Sussex Express
Media follow-up
An article in The Independent on 11th August by journalist Abbie Llewellyn followed up on the Adjournment Debate.
Other outlets which picked up on the WBTi Report launch and the debate:
ITV Regional News interviewed Jess Brown-Fuller regarding the outcome of the CMA report, (a market study on infant formula and follow-on formula) set to be released on 1st September 2025.
The i Paper ran an article by journalist Emma Morgan on infant formula marketing.
Parliament News magazine ran a piece by Jess Brown-Fuller MP: Building the ‘healthiest generation ever’ starts with making sure every child has a fair start in life.
The Nursing Times published an article about the WBTi Report launch and policy event, hosted by Jess Brown Fuller, highlighting quotes from iHV CEO Alison Morton, Vicky Sibson of First Steps Nutrition Trust, and Jess Brown-Fuller.
The British Medical Journal on 26 June included a further news article by Gareth Iacobucci, about the WBTi launch and our Call to Action for the government to implement the CMA recommendations in full: “Formula milk: Overpriced and misleading products are risking child health, say campaigners.” BMJ 2025; 389:r1333.
Other recent relevant contributions by Jess Brown-Fuller MP to Parliamentary debates
Prior to the Adjournment debate on 1st July there was a Parental Leave Review debate led by Justin Madders MP, the Parliamentary Under-Secretary of State for Business and Trade. Various members of the APPG on Infant Feeding attended the meeting. Jess Brown-Fuller asked about the impact of breastfeeding policies on mothers returning to work. Despite the WBTi findings that mothers are struggling with continuing to breastfeed upon return to work, Justin Madders explained that this fell slightly outside the scope of the review but he was happy to correspond on the matter.
On 7th July there was a debate on Giving Every Child the Best Start in Life Strategy, led by Bridget Phillipson MP, Secretary of State for Education. Jess Brown-Fuller asked for confirmation that Best Start centres will be firmly rooted in evidence-based feeding support. The Secretary of State gave an assurance.
Photo credit: Office of Jess Brown-Fuller MP
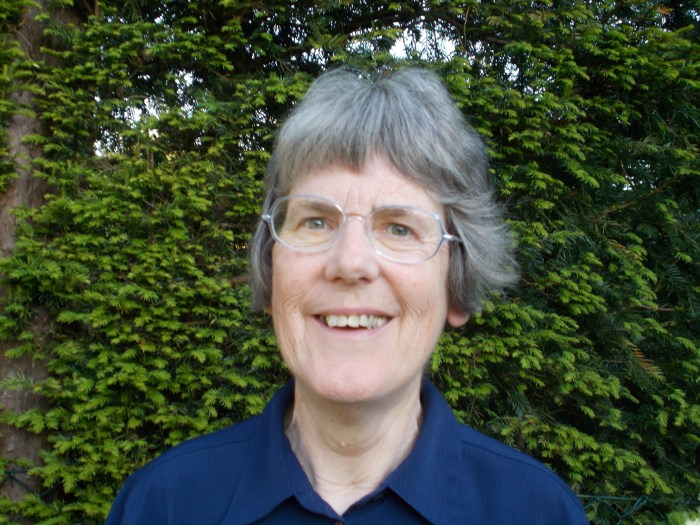
Jess Brown-Fuller MP looking at the WBTi Report with Clare Meynell
Author: Clare Meynell RM (rtd), IBCLC

Clare had a long career as a midwife and infant feeding lead achieving the UNICEF UK Baby Friendly Initiative Gold award accreditation at her local hospital. Currently, with Helen Gray, she jointly coordinates the UK WBTI working group and co-presented the first report for the UK in Parliament in November 2016 and the second in 2024.
Clare still volunteers her knowledge and experience at a regular mother and baby support group.
Her focus recently has been to create “Actions for Change” through the WBTi report recommendations so that the next generation of mothers are enabled to achieve their personal breastfeeding goals and that society better understands the health-giving properties of human milk as the physiologically normal first food for babies.